Augmented Reality sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a world where digital content seamlessly blends with our physical reality. Imagine trying on clothes virtually before purchasing them, exploring historical sites with interactive overlays, or receiving real-time guidance during complex surgical procedures.
This is the promise of augmented reality (AR), a technology that is rapidly transforming how we interact with the world around us.
AR overlays computer-generated images, sounds, and other sensory information onto our real-world view, creating a richer and more interactive experience. This technology leverages cameras, sensors, and powerful software to achieve this remarkable feat. From its humble beginnings in the 1960s, AR has evolved significantly, driven by advancements in computing power, mobile devices, and sophisticated algorithms.
Definition and History of Augmented Reality

Augmented reality (AR) is an interactive experience where computer-generated images are superimposed onto the user’s view of the real world, thereby enhancing the perception of reality. This technology has revolutionized various industries, offering immersive experiences and innovative applications.
Origins and Evolution of Augmented Reality
The concept of AR dates back to the 1960s, with the development of head-mounted displays (HMDs) that enabled users to see computer-generated imagery. One of the earliest demonstrations of AR technology was the “Sword of Damocles,” created by Ivan Sutherland at Harvard University in 1968.
This system used a head-mounted display to project a wireframe image of a room onto a user’s view, simulating a virtual environment.
“The Sword of Damocles” was a groundbreaking system that laid the foundation for modern AR technology.
The development of AR technology progressed steadily throughout the 1970s and 1980s, with researchers exploring various applications and refining the technology. A significant milestone was the development of the “Virtual Fixtures” system by the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory in the 1990s.
This system used AR to guide workers performing complex tasks, improving accuracy and efficiency.The 2000s witnessed a surge in the development and commercialization of AR technology, driven by advancements in computing power, mobile devices, and internet connectivity. The release of the ARToolkit software in 1999 provided a framework for developing AR applications, paving the way for widespread adoption.
Distinction between AR and VR
AR and VR are often confused, but they represent distinct technologies with different goals.
- Augmented Reality (AR)overlays computer-generated imagery onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of reality.
- Virtual Reality (VR)creates an immersive experience that completely replaces the real world with a computer-generated environment.
AR applications are designed to enhance the real world, while VR applications aim to transport users to virtual environments. AR allows users to interact with both the real and virtual worlds simultaneously, while VR isolates users from the real world.Examples of AR applications include:
- Mobile games like Pokémon GO, where virtual creatures are superimposed onto the real world.
- Navigation apps that provide real-time directions by overlaying virtual arrows onto the user’s view.
- Medical applications that allow surgeons to visualize internal organs during surgery.
Examples of VR applications include:
- Virtual reality games that immerse players in a simulated world.
- Training simulations that provide realistic experiences for various professions, such as flight training or surgical procedures.
- Virtual tours that allow users to explore destinations from the comfort of their homes.
How Augmented Reality Works
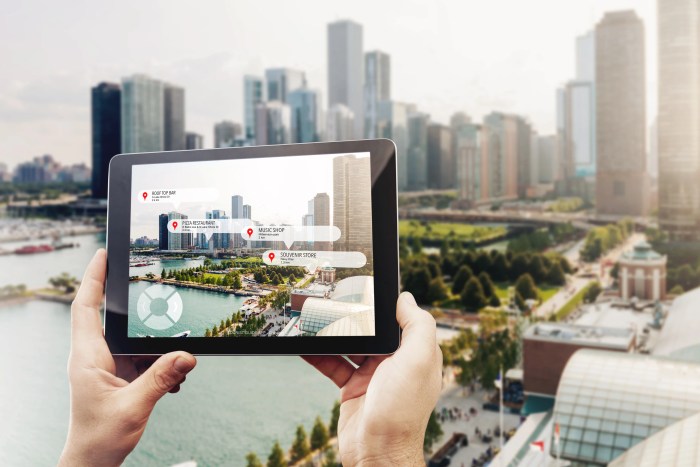

Augmented reality (AR) seamlessly blends the digital and physical worlds, enriching our perception of reality. This innovative technology utilizes sensors, cameras, and sophisticated software to overlay digital content onto our real-world view, creating an interactive and immersive experience.
The Fundamental Principles of AR
AR systems rely on a combination of hardware and software to achieve this seamless integration.
- Sensors:AR devices employ sensors such as accelerometers, gyroscopes, and compasses to track the user’s movements and orientation in space. These sensors provide real-time information about the user’s position and direction, enabling the AR system to accurately align digital content with the real world.
- Cameras:Cameras capture the real-world environment, providing visual input to the AR system. The captured images are then analyzed and processed by the software to identify objects and features in the real world.
- Software:AR software is the brain behind the technology. It processes data from sensors and cameras, interprets the user’s environment, and generates the digital content that is overlaid onto the real world. This software also manages the interaction between the user and the AR experience.
Overlaying Digital Content
AR systems utilize various techniques to overlay digital content onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of their surroundings.
- Image Recognition:This technique involves identifying and recognizing specific images or patterns in the real world. When the AR system detects a target image, it overlays digital content onto that image, creating an interactive experience. For example, a user could point their smartphone camera at a product packaging and see an interactive 3D model of the product superimposed on the packaging.
- Object Tracking:Object tracking enables AR systems to track the movement of real-world objects. This allows digital content to be dynamically overlaid onto the object as it moves, maintaining its position and orientation relative to the object. For example, in a gaming application, an AR system could track the movement of a physical game piece and display a virtual character or object that interacts with the piece.
Types of AR Experiences, Augmented Reality
AR experiences can be categorized into different types based on their implementation and the way they interact with the real world.
- Marker-based AR:This type of AR relies on visual markers, such as images or patterns, to trigger the overlay of digital content. When the camera detects a marker, the AR system overlays the corresponding digital content onto the marker’s location. Marker-based AR is often used in games, educational applications, and marketing campaigns.
For example, a user could point their smartphone camera at a magazine advertisement featuring a marker and see a 3D product model pop out of the page.
- Location-based AR:Location-based AR uses GPS data and other location-based information to overlay digital content onto the user’s real-world surroundings. This type of AR is commonly used in navigation apps, tourism guides, and location-based games. For example, a user could use a location-based AR app to see historical information about landmarks as they walk around a city.
- Projection-based AR:Projection-based AR projects digital content onto real-world surfaces using projectors. This type of AR is often used in interactive displays, entertainment, and advertising. For example, a user could walk past a storefront window with a projection-based AR display and see interactive product demonstrations projected onto the window.
Applications of Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) has rapidly evolved from a futuristic concept to a transformative technology with widespread applications across various industries. AR overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing our perception and interaction with our surroundings. This technology has the potential to revolutionize how we work, learn, shop, and entertain ourselves.
Applications Across Industries
AR’s versatility allows it to be integrated into diverse sectors, offering unique solutions and enhancing user experiences. The following table provides an overview of AR applications in various industries:
| Industry | AR Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Gaming |
|
|
| Healthcare |
|
|
| Education |
|
|
| Retail |
|
|
| Manufacturing |
|
|
Emerging Applications of AR
AR is rapidly evolving, and its potential applications are expanding into new and exciting fields. Some of the emerging areas where AR is expected to have a significant impact include:
- Tourism and Travel:AR can transform the way we experience travel by providing real-time information about destinations, landmarks, and cultural attractions. For instance, AR apps can overlay historical information, translate signage, and even offer interactive tours. This immersive experience can enhance traveler engagement and understanding of their surroundings.
- Real Estate:AR can revolutionize the real estate industry by allowing potential buyers to virtually walk through properties, visualize furniture placement, and experience the space as if they were physically present. This can help buyers make more informed decisions and reduce the need for multiple physical viewings.
- Architecture and Design:AR can empower architects and designers to visualize their creations in real-world contexts before construction begins. They can use AR to overlay 3D models of buildings and structures onto existing environments, allowing for better understanding of scale, proportion, and aesthetics.
This can lead to more efficient design processes and improved project outcomes.
- Social Interaction:AR has the potential to enhance social interaction by creating shared experiences and bridging physical distances. For example, AR apps can enable people to interact with virtual avatars of friends and family members, even if they are geographically separated. This could revolutionize how we communicate and connect with others, particularly in a world increasingly reliant on digital communication.
Benefits and Challenges of Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that has the potential to revolutionize the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us. It has numerous benefits that can enhance our lives in various ways, but it also comes with its own set of challenges that need to be addressed.
This section will delve into the advantages and limitations of AR, exploring its potential and its obstacles.
Advantages of Augmented Reality
AR offers a range of benefits that can significantly improve user experiences, boost efficiency, and unlock new possibilities for innovation. Here are some key advantages:
- Enhanced User Experience:AR can enrich user experiences by superimposing digital information onto the real world, making interactions more engaging and informative. For example, AR can be used to provide real-time product information, translate languages in real-time, or create interactive games and experiences.
- Improved Efficiency:AR can streamline processes and improve efficiency by providing workers with real-time information and guidance. For instance, AR can be used in manufacturing to guide workers through assembly processes, reducing errors and improving productivity.
- Increased Productivity:By providing workers with real-time information and guidance, AR can help them complete tasks more efficiently and accurately. This can lead to increased productivity and reduced costs.
- New Possibilities for Innovation:AR opens up new avenues for innovation by enabling the creation of interactive experiences, immersive simulations, and novel applications. This can lead to the development of new products, services, and business models.
Challenges of Augmented Reality
While AR offers significant potential, it also presents a number of challenges that need to be addressed for its widespread adoption and success. These challenges include:
- Cost:Developing and deploying AR applications can be expensive, requiring specialized hardware, software, and development expertise. This can be a barrier for small businesses and individuals.
- Accessibility:AR requires specialized hardware, such as smartphones or AR headsets, which can be expensive and may not be accessible to everyone. This can limit the reach and impact of AR technologies.
- Privacy Concerns:AR applications collect data about users’ locations, preferences, and interactions with the real world. This raises concerns about privacy and data security, as this information could be misused or compromised.
- Technical Limitations:Current AR technologies have limitations in terms of processing power, battery life, and display quality. These limitations can affect the performance and user experience of AR applications.
Final Summary
Augmented reality holds immense potential to revolutionize various aspects of our lives, from entertainment and education to healthcare and manufacturing. As the technology continues to mature, we can expect even more innovative and transformative applications. The future of AR is bright, promising a world where the lines between the physical and digital realms blur, opening up exciting possibilities for human interaction and exploration.
Questions Often Asked
What is the difference between augmented reality and virtual reality?
Augmented reality overlays digital information onto the real world, while virtual reality immerses users in a completely computer-generated environment.
How is augmented reality used in healthcare?
AR is used in healthcare for various purposes, including surgical guidance, medical training, and patient rehabilitation. For example, surgeons can use AR to visualize complex anatomy and overlay vital patient data during surgery.
What are some examples of popular augmented reality apps?
Popular AR apps include Pokémon GO, Snapchat filters, IKEA Place, and Google Maps’ Live View.